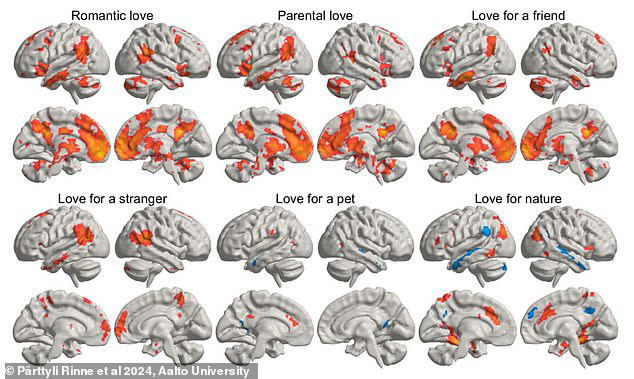
Love is not just a feeling but a complex brain phenomenon, newly revealed through groundbreaking brain imaging studies. Scientists have recently mapped where different types of love—romantic, maternal, and unconditional—are felt within the brain. These discoveries offer a profound insight into the neurological basis of our most cherished emotions.
The Science of Love
Using advanced brain imaging techniques, researchers have identified specific areas of the brain activated by different forms of love. This research highlights the complex and distinct neurological pathways that underpin our emotional experiences.
Romantic Love
Romantic love is characterized by intense passion and longing. Brain imaging studies show that romantic love activates regions of the brain associated with reward and motivation, such as the ventral tegmental area and the caudate nucleus. These areas are rich in dopamine, a neurotransmitter playing a crucial role in the brain’s reward circuitry. This suggests that romantic love is closely tied to our brain’s reward system, driving the feelings of euphoria and desire often associated with being in love.
Maternal Love
Maternal love, or the love a mother feels for her child, is one of the most powerful and enduring forms of love. Studies have found that maternal love activates areas of the brain involved in empathy, caregiving, and social bonding, such as the periaqueductal gray and oxytocin-rich regions. This underscores the deep biological roots of a mother’s bond with her child, highlighting the role of oxytocin—often referred to as the “love hormone”—in fostering this profound connection.
Unconditional Love
Unconditional love, often felt towards close friends, family members, or pets, engages different neural pathways than romantic or maternal love. Research shows that unconditional love activates brain regions associated with social attachment and altruism, such as the medial prefrontal cortex and the anterior cingulate cortex. This form of love is marked by selflessness and a sense of deep connection, illustrating the diverse ways our brains process different types of emotional bonds.
The Complexity of Human Emotions
These findings not only highlight the complexity of love but also offer a deeper understanding of how our emotions are intricately linked to our neurological systems. By mapping out where love is felt in the brain, scientists are uncovering the unique and interconnected neural networks that shape our emotional lives.
Implications for the Future
Understanding the neurological basis of love has significant implications for various fields, including psychology, neuroscience, and even artificial intelligence. By studying how different types of love are processed in the brain, researchers can develop new treatments for emotional and social disorders, enhance our understanding of human behavior, and improve the ways AI can interact with and understand human emotions.
Conclusion
The study of love in the brain is still in its early stages, but the discoveries made so far offer a fascinating glimpse into the complex and varied ways we experience love. As scientists continue to unravel the mysteries of our emotions, we can look forward to a deeper understanding of the human experience, enriching our appreciation for the myriad ways we connect with others.
For more on these groundbreaking discoveries, Click Here here.